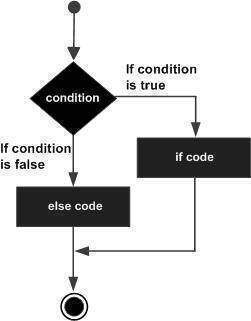
if语句后面可以是一个可选的else语句,当布尔表达式为false时执行这个可选的else语句。
Go编程语言中if…else语句的语法是
if(boolean_expression)
{
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */
}
else
{
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false */
}如果布尔表达式的计算结果为true,则将执行if代码块,否则将执行 else 代码块。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
/* local variable definition */
var a int = 100;
/* check the boolean condition */
if( a < 20 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
fmt.Printf("a is less than 20\n" );
} else {
/* if condition is false then print the following */
fmt.Printf("a is not less than 20\n" );
}
fmt.Printf("value of a is : %d\n", a);
}当上述代码被编译和执行时,它产生以下结果
a is not less than 20; value of a is : 100
if语句后面可以跟一个可选的else if ... else语句,这对于使用单个 if ... else if语句测试各种条件非常有用。
当使用if,else if,else语句有几点要记住:
一个if语句可以有零或一个else语句,但是它必须在else if语句之后。
一个if语句可以有零个或许多else if,并且它们必须在else语句之前。
当有一个else if测试匹配成功,剩余的任何else if或else语句都不会测试。
Go编程语言中的if ... else if ... else语句的语法是:
if(boolean_expression 1)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 2)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 3)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */
}
else
{
/* executes when the none of the above condition is true */
}package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
/* local variable definition */
var a int = 100
/* check the boolean condition */
if( a == 10 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
fmt.Printf("Value of a is 10\n" )
} else if( a == 20 ) {
/* if else if condition is true */
fmt.Printf("Value of a is 20\n" )
} else if( a == 30 ) {
/* if else if condition is true */
fmt.Printf("Value of a is 30\n" )
} else {
/* if none of the conditions is true */
fmt.Printf("None of the values is matching\n" )
}
fmt.Printf("Exact value of a is: %d\n", a )
}当上述代码被编译和执行时,它产生以下结果:
None of the values is matching Exact value of a is: 100